Japan is renowned for offering “advanced technology” and “safety and reliability” in the field of medical tourism. Among the various options available, DWIBS (Diffusion-weighted Whole-body Imaging with Background Suppression) has gained popularity among medical tourists from Asian countries due to its radiation-free nature and quick examination process. This article provides a detailed explanation of DWIBS, including its features, what it can and cannot detect, comparisons with other diagnostic methods, and the actual examination process.
What is DWIBS?
DWIBS (Diffusion-weighted Whole-body Imaging with Background Suppression) is a cutting-edge whole-body screening technology using high-performance MRI. Developed in 2004 by a Japanese physician, DWIBS visualizes abnormalities such as cancer and inflammation by detecting irregularities in the movement (diffusion) of water molecules within cells. The technology has been extensively studied and applied clinically in Japan and is now gaining global recognition.
Principles of DWIBS
DWIBS leverages MRI technology to visualize the movement of water molecules in the body. Cancer cells are denser than normal cells, restricting water molecule movement. By highlighting these differences, DWIBS can identify areas of abnormality and detect widespread lesions or metastases in a single scan.
Features of DWIBS
- Radiation-Free: Unlike CT or PET-CT, DWIBS does not use X-rays or radioactive tracers, making it a safer option.
- Short Examination Time: The scan takes approximately 30–60 minutes, significantly shorter than PET-CT.
- No Dietary Restrictions: Patients do not need to fast or manage insulin levels before the test, making it suitable for diabetic patients.
- Non-Invasive: The procedure does not require injections or invasive instruments, ensuring a comfortable experience.
Who Cannot Undergo DWIBS?
The following individuals may not be eligible for DWIBS:
- Metal Implants: Patients with pacemakers, artificial joints, or brain aneurysm clips.
- Tattoos or Permanent Makeup: Certain pigments containing metal components may cause heat reactions or discoloration during the scan.
- Pregnant Women: DWIBS may not be recommended due to potential risks to the fetus.
- Claustrophobia: Patients who feel anxious about lying in an enclosed MRI scanner for an extended period should consult their doctor beforehand.
What DWIBS “Can” and “Cannot” Detect
Detectable Conditions
DWIBS is capable of identifying the following conditions:
- Cancer: Colon cancer, pancreatic cancer, liver cancer, breast cancer, malignant lymphoma, etc. It is particularly effective for detecting lymph node metastases and bone metastases.
- Inflammation and Infections: Conditions such as sinusitis or osteomyelitis can also be detected.
- Benign Tumors: Lipomas and cysts are also visible on DWIBS scans.
Limitations
While DWIBS is highly effective for many conditions, it has certain limitations:
- Lung Cancer: Small lesions such as “ground-glass nodules” are better detected with CT scans.
- Stomach and Esophageal Cancer: Endoscopic examinations offer higher accuracy for these cancers.
- Early-stage Cancer: Small or low-density cancer cells may be missed.
Comparison Between DWIBS and PET-CT
DWIBS vs. PET-CT
Both DWIBS and PET-CT are used for whole-body screening but have distinct features:
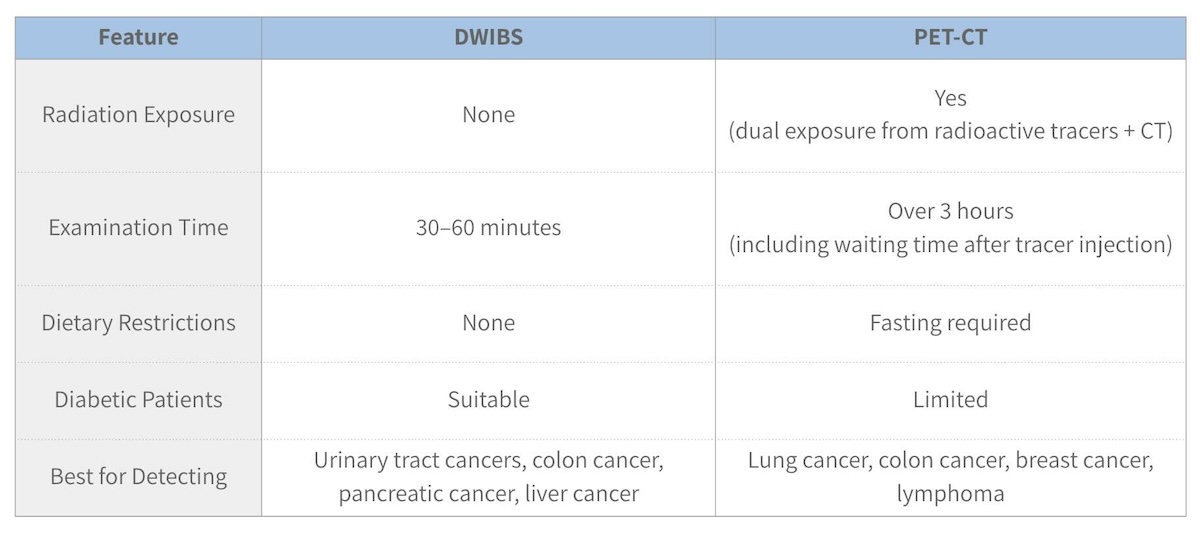
Strengths of DWIBS
- Radiation-Free Safety:
Since DWIBS does not use radiation, it is safe for children and pregnant women. - Suitable for Diabetic Patients:
Unlike PET-CT, which requires blood sugar management before the test, DWIBS has no such restrictions. - Comprehensive Health Evaluation:
In addition to detecting cancer, DWIBS can evaluate inflammation and benign tumors simultaneously.
Weaknesses of DWIBS
- Not Suitable for Air-Filled Organs like Stomach or Lungs:
The quality of images may decrease at air-tissue boundaries. - Limited Detection of Small Lesions or Early-stage Cancers:
Low-density cancer cells may not be easily identifiable on MRI images. - Requires Expert Interpretation:
Analyzing DWIBS images requires specialized knowledge from experienced radiologists.
Actual Examination Process
DWIBS scans are simple and quick but involve advanced MRI technology requiring preparation and specific procedures. Below is an overview of a typical process:
Step 1: Selecting a Medical Facility and Booking
For international patients, medical tourism facilitators often manage bookings and related procedures. These facilitators also handle language support. Major cities like Tokyo have facilities equipped with DWIBS technology.
Step 2: Examination Day
- Upon arrival at the facility, patients submit their medical history forms (translation support is available). After confirming the appointment details, they are guided to a changing room.
- Patients change into non-metallic clothing to avoid interference with the MRI machine. All metallic items such as jewelry or watches must be removed.
- The patient lies on the MRI table while specialized coils are placed around their body to enhance image quality. The scan takes 30–60 minutes during which patients are advised to remain still.
- Once the scan is complete, patients can resume normal activities immediately.
Step 3: Post-examination
Results are typically provided within two weeks via mail or online platforms. If abnormalities are detected, additional tests such as endoscopy or CT scans may be recommended.
Conclusion
DWIBS represents a groundbreaking advancement in whole-body health screening that combines safety with efficiency. Its radiation-free nature makes it particularly appealing to patients concerned about repeated exposure to X-rays or radioactive tracers. While it excels at detecting cancers like colon and pancreatic cancers as well as inflammation and benign tumors, it also has limitations when it comes to air-filled organs like the lungs or early-stage cancer detection.
For international patients considering medical tourism in Japan, DWIBS offers a unique opportunity to undergo advanced screening using state-of-the-art technology developed by Japanese experts. By pairing this diagnostic method with professional support from medical tourism facilitators who handle language barriers and logistical challenges, patients can experience seamless care during their visit.
Whether you’re seeking peace of mind through preventive health screening or addressing specific health concerns, Japan’s expertise in DWIBS ensures that you’ll receive world-class medical attention combined with unparalleled hospitality.
<References>
- Kenkoin Clinic. (2025). Whole-body MRI (DWIBS). Retrieved from https://www.kenkoin.jp/dwibs/
- Heiwadai Hospital Preventive Medicine Center. (2023). Guide to DWIBS Screening. Retrieved from https://www.sozokai-pmc.jp/news/dwibs/
- Japan Radiological Society. (2020). Imaging Guidelines. Retrieved from https://www.jcr.or.jp/
- Nippon.com. (2024). Medical Tourism and High Precision Health Screenings. Retrieved from https://www.nippon.com/
- JMHC (Japan Medical & Health Tourism Center). (2025). Medical Tourism Support Services. Retrieved from https://j-medical-healthcare.com/
